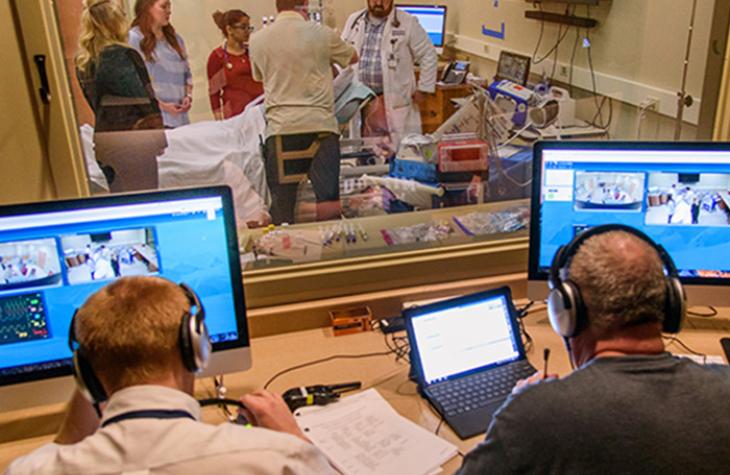
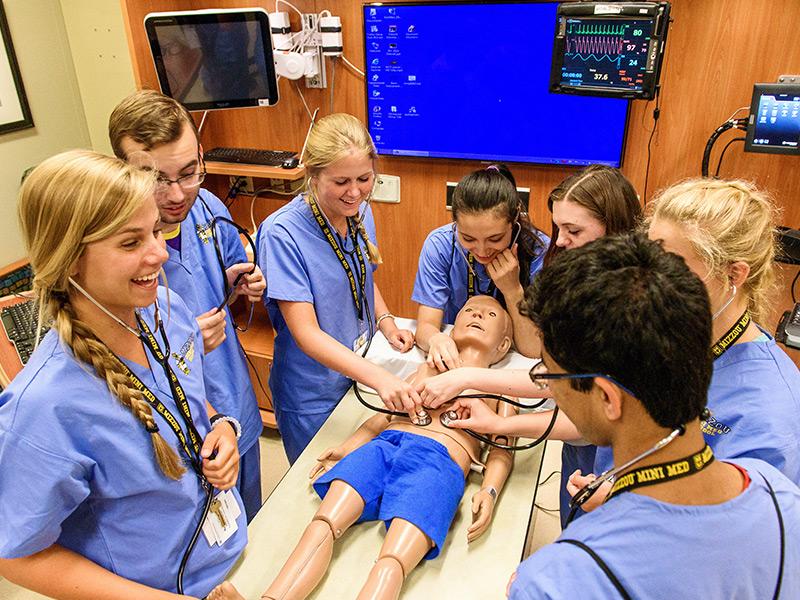
The MU School of Medicine offers three distinct learning tracks:
- Medical education for medical students;
- Graduate medical education for residents and fellows; and
- Master’s and doctoral degree programs in investigative areas from molecular microbiology and immunology to health management and informatics.
Students also may pursue a course of study that combines medicine and the basic sciences through the Tom and Anne Smith MD-PhD Program.
Students in each track benefit from patient-based learning, a style of medical education pioneered at the MU School of Medicine that emphasizes problem-solving, self-directed learning and early clinical experience.
Medical Students
The University of Missouri School of Medicine has expanded its medical school class size from 96 to 128 students to address a critical shortage of physicians in Missouri and the nation. MU’s medical school accepts students each year through a traditional application process and through the Lester R. Bryant Pre-Admissions Program for young people coming from rural backgrounds. Medical students spend their first two years at our Columbia campus and have the option to spend their third and fourth years in Columbia or at our Springfield Clinical Campus, which operates in partnership with CoxHealth and Mercy health systems. Learn more about our campus in Springfield, Missouri, and our class-expansion project.
The patient-based learning curriculum uses patient cases to teach medical students the basic sciences in the context of a real physician practice. The small-group learning environment is supported by early exposure to patient care, a rural program that offers clinical education in underserved areas and many other innovative programs. MU’s medical student program has been profiled in the Journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges, which has also published an extensive study on the success of MU’s curriculum.
Residents and Fellows
More than 30 percent of MU physician graduates stay at the university for its graduate medical education programs. MU’s medical school has more than 400 residents and fellows in nearly 50 specialty programs. The programs focus on the development of clinical skills, professional competencies and factual knowledge required by each specialty. The school’s residents and fellows benefit from a close association with other physicians, active participation in patient care and teaching, and a variety of opportunities to pursue their research interests.
Master’s and Doctoral Students
The medical school educates more than 200 students pursuing master’s and doctoral degrees each year. The degree programs include biochemistry, health management and informatics, medical pharmacology and physiology, molecular microbiology and immunology, nutrition and exercise physiology, and pathology and anatomical sciences. Students in these programs typically pursue a two- to five-year course of study that is interwoven with the scholarly activities of the faculty researchers in their degree programs. The Department of Family and Community Medicine offers an online master’s degree for physicians who want to pursue an academic career teaching and conducting research.
Practicing Physicians
The Office of Continuing Education for Health Professions (CEHP) addresses and responds to educational needs in Missouri not adequately addressed in other forums and by other providers with a particular focus on primary care physicians in rural areas through annual conferences targeting their particular needs. CME/PLL embodies high standards regarding the ethical conduct of CME activities that are consistent with the Guidelines of the ACCME and promote effective education.